Power outages have increasingly disrupted life across Spain in recent years, affecting major cities and rural communities alike.
Spain’s national electricity operator, Red Eléctrica de España (REE), reports that unexpected blackouts are no longer rare events but are becoming part of the challenges associated with climate shifts, infrastructure ageing, and rising energy demand.
What, then, lies behind the latest widespread power disruptions across the Iberian Peninsula?
What Has Caused the Recent Widespread Power Outages in Spain?
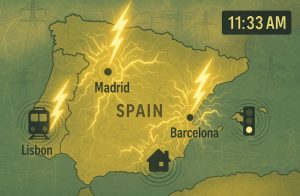
On Monday, 28 April 2025, a massive power cut plunged Spain, Portugal, and parts of south-western France into darkness.
Major urban hubs including Madrid, Barcelona, and Lisbon were severely affected, halting public transport, suspending events such as the Madrid Open tennis tournament, and forcing millions to adapt swiftly to life without electricity.
The blackout, referred to by REE as “el cero” meaning “the zero” began around 11:33 am Western European Summer Time. Within hours, authorities initiated recovery procedures, cautiously restoring voltage across northern, southern, and western regions to avoid overwhelming the fragile system.
Early concerns hinted at potential cyberattacks, prompting emergency meetings of Spain’s National Security Council and Portugal’s government. However, European officials, including the President of the European Council, António Costa, quickly confirmed that there was no evidence of malicious activity.
Investigations found that an unusual atmospheric event was at the heart of the failure. Extreme temperature variations within the interior of Spain caused oscillations in very high voltage (400 kV) lines, a rare but known phenomenon in the electrical industry called induced atmospheric vibration.
These vibrations led to synchronisation failures between interconnected European energy networks, triggering cascading power plant disconnections and widespread outages.
What Are the Common Reasons Behind Spain’s Power Outages?
While the April 2025 incident was extraordinary, it reflects broader systemic vulnerabilities that Spain faces today. Among the most frequent causes of outages are:
- Severe weather events such as heatwaves, storms, and floods
- Infrastructure ageing and delayed modernisation of the energy grid
- High demand peaks resulting in load shedding or rolling blackouts
- Atmospheric anomalies causing physical disruptions to transmission lines
- Complexities associated with interconnected European grids
Although each cause on its own can be managed, their convergence, particularly during extreme weather events, increases the risk of extensive blackouts.
How Does the Spanish National Grid Handle Power Failures?

Spain’s electrical system, coordinated by REE, is designed to manage occasional outages. In the event of a major disruption, several procedures are set into motion.
Grid operators closely monitor frequency stability, a crucial measure since a drop below the European standard of 50Hz can result in automatic shutdowns of power stations.
When an imbalance occurs, REE enacts load-shedding strategies, systematically reducing consumption in specific regions to stabilise the overall grid.
Emergency teams are dispatched to critical infrastructure points, ensuring damaged substations or transformers are repaired promptly. In large-scale events, voltage is restored gradually to prevent overloading newly energised sections of the grid.
The response in April 2025 demonstrated both the strengths and limitations of Spain’s contingency planning. Although recovery was largely successful by the next morning, isolated regions continued to face prolonged difficulties.
How Is Spain’s Energy Crisis Impacting the Electricity Supply?
Spain’s ambitious transition toward renewable energy, while largely successful, has created new balancing challenges. In 2024, renewable sources accounted for 56% of the country’s electricity production, a figure set to rise to 81% by 2030.
However, reliance on intermittent sources such as solar and wind introduces unpredictability. Traditional energy balancing relied heavily on spinning reserves like gas turbines, which could be ramped up or down quickly.
In contrast, solar and wind outputs vary with weather conditions, complicating real-time supply and demand matching.
Moreover, global energy market volatility and dependency on imports for fossil fuels have further strained Spain’s energy resilience.
In response, significant investments are being channelled into energy storage solutions such as advanced batteries and flywheels, and into smart grids capable of automatically managing frequency fluctuations.
How Do Weather Extremes Cause Power Outages in Spain?

The Iberian Peninsula’s diverse and often extreme climate presents several challenges to grid reliability.
Heatwaves not only increase energy consumption due to air-conditioning use but can also physically impact infrastructure, causing cables to sag and substations to overheat. Conversely, severe storms can tear down overhead lines and flood critical electrical facilities.
The April 2025 blackout stands as a case study of another risk—induced atmospheric vibrations caused by dramatic temperature shifts.
These oscillations destabilised high-voltage transmission lines, leading to cascading effects that could not be contained by national boundaries.
Historically, Spain has also faced prolonged droughts that impair hydroelectric generation, further exacerbating electricity shortages.
The combined pressure from environmental factors highlights the urgent need for climate adaptation measures within the national grid strategy.
How Long Do Power Outages Typically Last in Spain?
The length of power outages in Spain depends on several factors, including the severity of the incident, geographical location, and the underlying cause.
In metropolitan centres such as Madrid or Barcelona, most outages are resolved within a few hours due to better infrastructure and faster emergency response.
However, in rural and mountainous regions, disruptions can last from 24 to 72 hours, particularly if access is hindered by weather or road conditions.
During the April 2025 blackout, Portugal’s grid operator, REN, reported full restoration by the following morning.
In Spain, REE restored power to the majority of areas overnight, though scattered communities remained offline well into Tuesday afternoon.
What Should You Do During a Power Cut in Spain?
Coping with a blackout requires a combination of preparation and caution. In the event of an outage:
- Stay informed through a battery-operated radio or official mobile apps if internet access remains available.
- Minimise mobile phone use to preserve battery life for emergencies.
- Avoid opening refrigerators and freezers to keep food fresh longer.
- Prepare emergency kits with bottled water, flashlights, spare batteries, basic medicines, and non-perishable foods.
- Report outages to your local energy supplier and follow government safety advisories.
For travellers, it is also advisable to carry cash, as ATMs and electronic payment systems often fail during widespread blackouts.
What Are the Preventive Measures to Reduce Future Blackouts in Spain?

Spain’s future energy security hinges on multiple strategic initiatives. Among the top priorities are:
- Expansion and integration of renewable energy sources across the grid
- Modernisation of ageing infrastructure including substations, transformers, and transmission lines
- Development of decentralised energy storage projects to smooth supply fluctuations
- Strengthening of international interconnections to provide mutual support during crises
International connectivity, while introducing the risk of cross-border disturbances, also offers a buffer against local failures escalating into full national crises.
Spain’s links with France, for instance, enabled faster stabilisation during the April 2025 incident.
Long-term resilience, however, will depend on substantial investment and technological innovation, including advanced frequency regulation tools and digital control networks.
Quick Overview of Major Spanish Power Outages in Recent Years
| Year | Cause | Affected Areas | Duration |
| 2020 | Storm Gloria | Catalonia, Valencia | 2–5 days |
| 2021 | Heatwave surge | Andalusia, Madrid | Several hours |
| 2022 | Infrastructure failure | Northern Spain | 8–12 hours |
| 2025 | Atmospheric anomalies | Spain, Portugal, SW France | 12–24 hours |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of power cuts in Spain?
Power cuts in Spain often result from extreme weather events, ageing grid infrastructure, atmospheric anomalies, and high peak energy demand.
How frequent are blackouts in Spanish cities?
Although infrequent, major cities like Madrid and Barcelona have experienced outages during periods of extreme weather or grid failures.
Can weather events like heatwaves trigger power failures?
Yes, particularly during heatwaves, the surge in electricity demand for cooling can overwhelm the system, leading to controlled blackouts.
What regions in Spain experience the most outages?
Rural regions and isolated areas, particularly in the north and along coastal zones, tend to experience longer and more frequent power outages.
Is Spain’s energy grid prepared for future crises?
Spain is making progress through renewable energy projects and grid modernisation, but experts argue that further investment is critical.
How do Spanish authorities manage large-scale blackouts?
Authorities use a combination of emergency load-shedding, gradual voltage restoration, public communication, and international cooperation to manage crises.
What emergency tips should travellers know during a blackout in Spain?
Travellers should carry portable chargers, have access to cash, limit travel, and stay informed through trusted local news sources.






