NMN, short for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, has rapidly gained traction in the world of longevity, biohacking, and wellness. Marketed as a powerful NAD+ precursor, it has been associated with claims of reversing signs of ageing, improving metabolism, and boosting energy.
These benefits have made NMN one of the most talked-about supplements in recent years.
However, as its popularity has grown, so has scrutiny. A growing number of users have reported mixed results some praising it as a breakthrough supplement, others deciding to discontinue its use altogether.
So why would someone stop taking NMN, especially after experiencing its supposed benefits?
This article provides a comprehensive look at NMN, what it does, why it’s taken, and most importantly, what can happen when people choose to stop using it.
What Is NMN?
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide is a naturally occurring compound in the human body. It plays a vital role in the biosynthesis of NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a coenzyme found in every cell.
NAD+ is essential for energy production, cellular repair, DNA integrity, and metabolic regulation.
As people age, NAD+ levels decline significantly, leading to reduced mitochondrial efficiency and an increased risk of age-related diseases.
NMN, by acting as a precursor to NAD+, promises to restore these levels, supporting various cellular functions and slowing the signs of biological ageing.
Why Has NMN Gained So Much Attention Recently?
The buzz surrounding NMN started in the scientific community, with research into how NAD+ influences ageing and metabolism.
One of the most influential figures in this space is Harvard professor Dr David Sinclair, who publicly discussed the potential of NMN to extend lifespan in animal models.
Several studies on mice suggested that NMN supplementation could:
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Enhance mitochondrial function
- Reduce markers of ageing
More recently, small-scale human trials have provided some promising results. For example, a study involving postmenopausal women with prediabetes showed improved insulin signalling after 10 weeks of NMN supplementation.
Another trial observed that amateur runners taking NMN experienced increased oxygen utilisation and endurance.
These findings, although preliminary, have fuelled public interest and increased sales of NMN products across global markets, including the UK.
Moreover, combinations such as NMN paired with Resveratrol a plant compound that activates the SIRT1 gene linked to longevity have been marketed as powerful longevity stacks, often advertised with phrases like “cellular rejuvenation” and “anti-ageing support.”
What Motivated People to Start Taking NMN Supplements?

The primary motivation behind NMN supplementation is to combat the natural decline in NAD+ levels that occurs with age.
As this decline affects energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cognitive function, many individuals particularly those in their 40s and older turn to NMN in hopes of rejuvenating their bodies at the cellular level.
Additional motivations include:
- The desire for better physical endurance and stamina
- Improving metabolic health, particularly for those with prediabetes or insulin resistance
- Enhancing cognitive clarity and memory
- Slowing down the perceived signs of ageing
People who follow fitness trends or biohacking communities are especially likely to adopt NMN supplements, often combining them with other longevity compounds like Resveratrol or Quercetin to maximise potential benefits.
What Side Effects or Issues Did Users Encounter With NMN?
Despite the potential benefits, not all users have a smooth experience with NMN. While many tolerate it well, others have reported side effects that made them question whether the supplement was suitable for long-term use.
Common side effects include:
- Sleep disturbances, particularly when taken later in the day
- Digestive discomfort, such as bloating or mild diarrhoea
- Skin sensitivity, including itching or redness
- Mild respiratory symptoms, such as nasal congestion
These effects tend to vary based on individual physiology, dosage, and whether the supplement is taken with food.
Most side effects are considered mild and transient, but in some cases, they can be significant enough to prompt discontinuation.
Another growing concern is tolerance build-up. Several long-term users have reported that the noticeable benefits such as increased energy or focus seem to plateau or even decline after several months, despite maintaining the same dosage.
Why Did NMN Results Disappoint Some Users Over Time?
The enthusiasm around NMN is often influenced by testimonials and anecdotal experiences rather than long-term clinical data.
As a result, users sometimes have unrealistic expectations, expecting dramatic improvements in health, energy, or appearance.
For many, the initial effects of NMN more energy, sharper focus, or better workouts can be real but short-lived. Over time, as NAD+ levels stabilise or the body adapts, those effects may diminish.
When this happens, users begin to question whether the supplement is worth the financial cost, especially if it’s not producing sustained, measurable results.
Additionally, because ageing is a complex process influenced by genetics, environment, and lifestyle, it’s unlikely that a single supplement even one as promising as NMN can serve as a catch-all solution.
What Are the Risks and Dangers of Taking NMN Supplements?

While there are currently no known severe health risks associated with NMN, there are some valid concerns surrounding its use, particularly in the context of long-term supplementation.
First, human trials are still limited, and many of the positive outcomes observed have been in animal models. This makes it difficult to predict the long-term impact of regular NMN use in humans.
Second, NMN is not subject to strict regulation in many countries, including the UK. This means:
- Product quality and purity can vary between brands
- Labelling might not always reflect actual dosages
- Contaminants or fillers could be present in some formulations
Lastly, some users rely on NMN as a substitute for healthy habits. While it can support cellular energy, it cannot compensate for a poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, or chronic stress.
What Happens When You Stop Taking NMN?
Discontinuing NMN does not cause withdrawal symptoms, but it can lead to gradual physiological changes as the body adjusts to the absence of the supplement.
NAD+ levels, which were elevated during supplementation, will begin to decline over time.
Energy Dynamics
One of the first changes noticed by former users is a reduction in energy levels. NMN helps support ATP production, which fuels cellular activity. Without the supplement, this process may slow temporarily until the body recalibrates.
Metabolic Adjustments
Some metabolic pathways may function less efficiently without NMN, particularly those related to glucose metabolism and mitochondrial activity. This may manifest as lower exercise tolerance or mild fatigue.
Ageing and Cellular Resilience
Although stopping NMN won’t accelerate ageing, it may reduce the body’s capacity to repair damage and respond to cellular stress as efficiently.
Users who felt more youthful or vibrant while on NMN might feel a slight decline in resilience, although they are simply returning to their natural baseline.
Immune Function
NAD+ is also involved in the immune response. Discontinuing NMN might result in subtle changes in how the immune system reacts to illness or inflammation. However, these effects are generally mild and often go unnoticed.
How Long Does It Take for NAD+ Levels to Return to Normal?
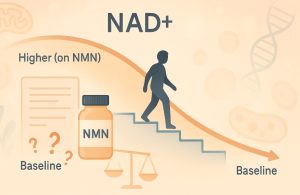
After stopping NMN, NAD+ levels tend to return to their pre-supplementation baseline within a few days to several weeks. The exact timeline depends on:
- Age and baseline NAD+ levels
- Previous NMN dosage and duration of use
- Diet and physical activity levels
- Overall health and stress management
Individuals who maintain healthy lifestyle habits such as intermittent fasting, exercise, and whole-food diets may experience a slower decline and maintain better cellular function even after stopping NMN.
What’s a Good NMN Supplement Alternative?
For those who decide to discontinue NMN but wish to maintain support for cellular energy, several alternative options exist.
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) is another NAD+ precursor that has been extensively studied and may offer comparable benefits.
Unlike NMN, NR requires an additional conversion step to become NAD+ but is known for its effectiveness and strong safety profile.
Resveratrol, often combined with NMN, can activate sirtuins—proteins involved in longevity and cellular repair. It supports NAD+ production indirectly and may also provide cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Quercetin and Fisetin are flavonoids found in fruits and vegetables that act as senolytics. They help the body clear out senescent cells, which contribute to chronic inflammation and tissue ageing.
Though they do not increase NAD+ directly, they complement longevity strategies effectively.
Other Ways to Support NAD+ Levels Naturally

Supplements are only part of the picture. A holistic approach to health can naturally support NAD+ levels and promote longevity without reliance on synthetic products.
- Regular Exercise: Aerobic workouts stimulate mitochondrial health and NAD+ synthesis
- Intermittent Fasting: Caloric restriction activates similar longevity pathways as NMN
- Nutrient-Dense Diet: Foods rich in Vitamin B3 (niacin), leafy greens, fish, and whole grains can support metabolic health
Combining these habits creates a sustainable foundation for cellular wellbeing and long-term energy maintenance.
What Changed After I Stopped Taking NMN?
| Aspect | Experience During Use | After Stopping NMN |
| Energy Levels | Mild increase initially | Slight decline, then stable |
| Sleep Quality | Occasionally disrupted | Improved |
| Cognitive Performance | No major change | Maintained |
| Side Effects | Mild fatigue, restlessness | Resolved |
| Overall Satisfaction | Moderate | Prefer a natural approach |
FAQs
Does stopping NMN cause a health setback?
No. Most people simply return to their pre-supplementation baseline, though it may feel like a drop after experiencing enhanced energy.
Can NMN be harmful long-term?
There’s currently no evidence suggesting serious long-term harm, but research in humans remains limited.
Will lifestyle habits maintain NAD+ after stopping NMN?
Yes, exercise, fasting, and a balanced diet can help sustain NAD+ production naturally.
Is NR a better option than NMN?
It depends. NR is more researched, but NMN is more direct. Some prefer NR due to its wider availability and stability.
Should I stop NMN if I feel no benefits?
If you’re not noticing changes after several months, it may be worth evaluating alternatives or discussing options with a health professional.
Are there signs your NAD+ is low?
Symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, and reduced exercise capacity could indicate lower NAD+, though these are non-specific.
What age is best to start NMN?
Most research focuses on middle-aged and older adults. Younger individuals may not need it unless NAD+ levels are clinically low.